 Genealogy Reference
Genealogy Reference
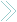
 Relationship Chart
Relationship Chart
California Settlers
 Genealogy Reference
Genealogy Reference
 Relationship Chart
Relationship Chart |
About/Contact |
 See Another chart below and an See example. Cousins 1st, 2nd & 3rd cousins etc. are on the same generation level as yourself. For example if you have common Grandparents, then you are equally 2 generations away making you 1st cousins. If you have common great-grandparents, then you are equally 3 generations away making you 2nd cousins. Cousin or First Cousin: You are a cousin or first cousin to the child of your uncle or aunt. Second Cousin: Your are a second cousin to the children of your parents' first cousins. Removed: Used to describe a difference in generations. "once removed" means that there is a difference of one generation. First cousin Once Removed: You are a first cousin once removed to the children of your first cousins and the parents of your second cousin (your parents first cousin). Second Cousin once Removed: The child of one's second cousin is a second cousin once removed, sometimes called third cousin.
Cousin relationships are reciprocal. i.e. Your relation to a cousin
To determine the relation for a cousin older than you.
Other (technically incorrect) uses of Cousin-
While the definition alludes to friendship and marriage as definitions Great-Uncle/Aunt: A brother/sister to any of one's grandparents.
In-laws
1. the sister of my spouse, or
However Aunt, Uncle, Niece and Nephew can apply to your spouses relatives also.
Step and Half Relataionships
Example
1 John FINLEY (b. 8 JUN 1579 (b.lchrystie, Scot.; d: 1670)
2 James FINLEY (b. 9 SEP 1631 Inchervie, Fife, Scot.; d: 16 FEB 1681 Inchervie, Fife)
| 3 Alexander FINLEY (b. 30 JUL 1667 Inchervie, St. Andrew's, Fife, Scot. d: 28 JAN 1736 Dublin Ire)
| 4 James Finley (b. 1687/8, Dublin, Ireland; d. 1753 Green Twp., Cmbr Co., PA)
| 5 William Finley (b. 1712, Dublin, Ireland; d. 1789 Augusta Co., VA)
| 6 John Finley (b. 15 Dec 1737 in Augusta Co,VA; d. (b.f 25 OCT 1802 in Augusta Co,VA)
| 7 James Finley (b. 1783, Staunton, Augusta Co., VA; d. 1866, Lincoln Co., MO)
| 8 Andrew Ramsey Finley (b. 1818, Shelbyville, KY; d. 1896, Santa Ana, CA)
| 9 Martha Emma Finley (b. 1856, Troy, MO; d. 1947, Santa Ana, CA)
| (Emma is Generation 6 in my table working back from the current generation)
2 Robert FINLEY (b. 1634 Incharvie,Fife, Scot.; d: 18 JUN 1712 in Armagh County, Ire)
3 Michael FINLEY (b. 7 MAY 1683 Co. Armagh, Ire; d. 1747 Sadsbury Twp., Chester Co., PA)
4 Rev. Samuel FINLEY (b. 2 Jul 1715 in Armaugh Co., Ire; d. 17 Jul 1766 in Philadelphia, PA)
[Was 5th president of The College of New Jersey (now Princeton U.) 1761-1766]
5 Rebecca (b. 1745 Nottingham, Cecil, MD; d. 1770 Monmouth NJ)
+Samuel Breese (b. 1737 in Shrewsbury, Monmouth, NJ; 1802 in Shrewsbury, NJ)
6 Elizabeth Ann Breese (b. 1766 New York, NY; d. 1828 New Haven, CT)
+ Rev. Jedidiah Morse (b. 1761 Woodstock, CT; d. 1826/28 New Haven, CT)
7 Samuel Finley Breese Morse (b. 1791 Charlestown, MA ;d. 1872 New York City)
Invented the Telegraph
4 Rev. James FINLEY (b. 4 Feb 1724 in Armaugh Co., Ire; d. 1795 Rehoboth Twp, PA)
[Original draft of Declaration of Independence was made in his Philadelphia home.]
In the above example, James and Robert are brothers, Alexander and Michael are
first cousins, James (1687) and Samuel are second cousins, Martha Emma and Samuel Finley are second cousins 5 times removed, Martha Emma and Samuel Morse are fifth cousins twice removed.
To find the relation between 9. Martha and 7. Samuel Morse.
Another Chart from www.genealogy.com/16_cousn.html
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Links: genealogy.com/ Nevárez Family Page Relationship Terms at Oak Road Syst. The Generic Family Tree Return to Califorina Settlers. |